forked from mindspore-Ecosystem/mindspore
325 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
325 lines
14 KiB
Markdown
# Contents
|
||
|
||
- [GoogleNet Description](#googlenet-description)
|
||
- [Model Architecture](#model-architecture)
|
||
- [Dataset](#dataset)
|
||
- [Features](#features)
|
||
- [Mixed Precision](#mixed-precision)
|
||
- [Environment Requirements](#environment-requirements)
|
||
- [Quick Start](#quick-start)
|
||
- [Script Description](#script-description)
|
||
- [Script and Sample Code](#script-and-sample-code)
|
||
- [Script Parameters](#script-parameters)
|
||
- [Training Process](#training-process)
|
||
- [Training](#training)
|
||
- [Distributed Training](#distributed-training)
|
||
- [Evaluation Process](#evaluation-process)
|
||
- [Evaluation](#evaluation)
|
||
- [Model Description](#model-description)
|
||
- [Performance](#performance)
|
||
- [Evaluation Performance](#evaluation-performance)
|
||
- [Inference Performance](#evaluation-performance)
|
||
- [How to use](#how-to-use)
|
||
- [Inference](#inference)
|
||
- [Continue Training on the Pretrained Model](#continue-training-on-the-pretrained-model)
|
||
- [Transfer Learning](#transfer-learning)
|
||
- [Description of Random Situation](#description-of-random-situation)
|
||
- [ModelZoo Homepage](#modelzoo-homepage)
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [GoogleNet Description](#contents)
|
||
|
||
GoogleNet, a 22 layers deep network, was proposed in 2014 and won the first place in the ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2014 (ILSVRC14). GoogleNet, also called Inception v1, has significant improvement over ZFNet (The winner in 2013) and AlexNet (The winner in 2012), and has relatively lower error rate compared to VGGNet. Typically deeper deep learning network means larger number of parameters, which makes it more prone to overfitting. Furthermore, the increased network size leads to increased use of computational resources. To tackle these issues, GoogleNet adopts 1*1 convolution middle of the network to reduce dimension, and thus further reduce the computation. Global average pooling is used at the end of the network, instead of using fully connected layers. Another technique, called inception module, is to have different sizes of convolutions for the same input and stacking all the outputs.
|
||
|
||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.4842): Christian Szegedy, Wei Liu, Yangqing Jia, Pierre Sermanet, Scott Reed, Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Vincent Vanhoucke, Andrew Rabinovich. "Going deeper with convolutions." *Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition*. 2015.
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Model Architecture](#contents)
|
||
|
||
The overall network architecture of GoogleNet is shown below:
|
||
|
||
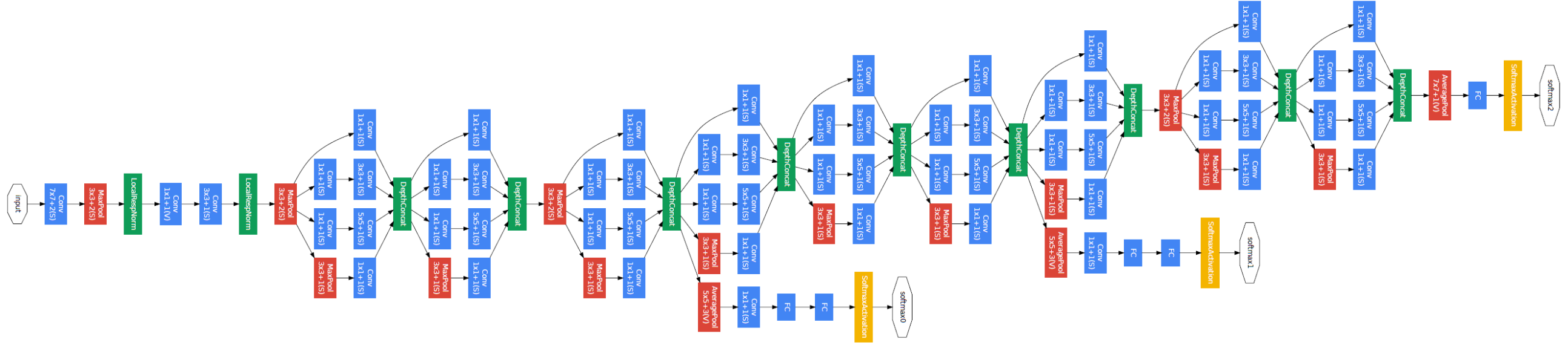
|
||
|
||
Specifically, the GoogleNet contains numerous inception modules, which are connected together to go deeper. In general, an inception module with dimensionality reduction consists of **1×1 conv**, **3×3 conv**, **5×5 conv**, and **3×3 max pooling**, which are done altogether for the previous input, and stack together again at output.
|
||
|
||

|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Dataset](#contents)
|
||
|
||
Dataset used: [CIFAR-10](<http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html>)
|
||
|
||
- Dataset size:175M,60,000 32*32 colorful images in 10 classes
|
||
- Train:146M,50,000 images
|
||
- Test:29.3M,10,000 images
|
||
- Data format:binary files
|
||
- Note:Data will be processed in dataset.py
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Features](#contents)
|
||
|
||
## Mixed Precision
|
||
|
||
The [mixed precision](https://www.mindspore.cn/tutorial/zh-CN/master/advanced_use/mixed_precision.html) training method accelerates the deep learning neural network training process by using both the single-precision and half-precision data formats, and maintains the network precision achieved by the single-precision training at the same time. Mixed precision training can accelerate the computation process, reduce memory usage, and enable a larger model or batch size to be trained on specific hardware.
|
||
For FP16 operators, if the input data type is FP32, the backend of MindSpore will automatically handle it with reduced precision. Users could check the reduced-precision operators by enabling INFO log and then searching ‘reduce precision’.
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Environment Requirements](#contents)
|
||
|
||
- Hardware(Ascend/GPU)
|
||
- Prepare hardware environment with Ascend or GPU processor. If you want to try Ascend , please send the [application form](https://obs-9be7.obs.cn-east-2.myhuaweicloud.com/file/other/Ascend%20Model%20Zoo%E4%BD%93%E9%AA%8C%E8%B5%84%E6%BA%90%E7%94%B3%E8%AF%B7%E8%A1%A8.docx) to ascend@huawei.com. Once approved, you can get the resources.
|
||
- Framework
|
||
- [MindSpore](http://10.90.67.50/mindspore/archive/20200506/OpenSource/me_vm_x86/)
|
||
- For more information, please check the resources below:
|
||
- [MindSpore tutorials](https://www.mindspore.cn/tutorial/zh-CN/master/index.html)
|
||
- [MindSpore API](https://www.mindspore.cn/api/zh-CN/master/index.html)
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Quick Start](#contents)
|
||
|
||
After installing MindSpore via the official website, you can start training and evaluation as follows:
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
# run training example
|
||
python train.py > train.log 2>&1 &
|
||
|
||
# run distributed training example
|
||
sh scripts/run_train.sh rank_table.json
|
||
|
||
# run evaluation example
|
||
python eval.py > eval.log 2>&1 & OR sh run_eval.sh
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Script Description](#contents)
|
||
|
||
## [Script and Sample Code](#contents)
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
├── model_zoo
|
||
├── README.md // descriptions about all the models
|
||
├── googlenet
|
||
├── README.md // descriptions about googlenet
|
||
├── scripts
|
||
│ ├──run_train.sh // shell script for distributed
|
||
│ ├──run_eval.sh // shell script for evaluation
|
||
├── src
|
||
│ ├──dataset.py // creating dataset
|
||
│ ├──googlenet.py // googlenet architecture
|
||
│ ├──config.py // parameter configuration
|
||
├── train.py // training script
|
||
├── eval.py // evaluation script
|
||
├── export.py // export checkpoint files into geir/onnx
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## [Script Parameters](#contents)
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
Major parameters in train.py and config.py are:
|
||
|
||
--data_path: The absolute full path to the train and evaluation datasets.
|
||
--epoch_size: Total training epochs.
|
||
--batch_size: Training batch size.
|
||
--lr_init: Initial learning rate.
|
||
--num_classes: The number of classes in the training set.
|
||
--weight_decay: Weight decay value.
|
||
--image_height: Image height used as input to the model.
|
||
--image_width: Image width used as input the model.
|
||
--pre_trained: Whether training from scratch or training based on the
|
||
pre-trained model.Optional values are True, False.
|
||
--device_target: Device where the code will be implemented. Optional values
|
||
are "Ascend", "GPU".
|
||
--device_id: Device ID used to train or evaluate the dataset. Ignore it
|
||
when you use run_train.sh for distributed training.
|
||
--checkpoint_path: The absolute full path to the checkpoint file saved
|
||
after training.
|
||
--onnx_filename: File name of the onnx model used in export.py.
|
||
--geir_filename: File name of the geir model used in export.py.
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
## [Training Process](#contents)
|
||
|
||
### Training
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
python train.py > train.log 2>&1 &
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
The python command above will run in the background, you can view the results through the file `train.log`.
|
||
|
||
After training, you'll get some checkpoint files under the script folder by default. The loss value will be achieved as follows:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# grep "loss is " train.log
|
||
epoch: 1 step: 390, loss is 1.4842823
|
||
epcoh: 2 step: 390, loss is 1.0897788
|
||
...
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
The model checkpoint will be saved in the current directory.
|
||
|
||
### Distributed Training
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
sh scripts/run_train.sh rank_table.json
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
The above shell script will run distribute training in the background. You can view the results through the file `train_parallel[X]/log`. The loss value will be achieved as follows:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# grep "result: " train_parallel*/log
|
||
train_parallel0/log:epoch: 1 step: 48, loss is 1.4302931
|
||
train_parallel0/log:epcoh: 2 step: 48, loss is 1.4023874
|
||
...
|
||
train_parallel1/log:epoch: 1 step: 48, loss is 1.3458025
|
||
train_parallel1/log:epcoh: 2 step: 48, loss is 1.3729336
|
||
...
|
||
...
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
## [Evaluation Process](#contents)
|
||
|
||
### Evaluation
|
||
|
||
Before running the command below, please check the checkpoint path used for evaluation. Please set the checkpoint path to be the absolute full path, e.g., "username/googlenet/train_googlenet_cifar10-125_390.ckpt".
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
python eval.py > eval.log 2>&1 &
|
||
OR
|
||
sh scripts/run_eval.sh
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
The above python command will run in the background. You can view the results through the file "eval.log". The accuracy of the test dataset will be as follows:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# grep "accuracy: " eval.log
|
||
accuracy: {'acc': 0.934}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Note that for evaluation after distributed training, please set the checkpoint_path to be the last saved checkpoint file such as "username/googlenet/train_parallel0/train_googlenet_cifar10-125_48.ckpt". The accuracy of the test dataset will be as follows:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# grep "accuracy: " dist.eval.log
|
||
accuracy: {'acc': 0.9217}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Model Description](#contents)
|
||
## [Performance](#contents)
|
||
|
||
### Evaluation Performance
|
||
|
||
| Parameters | GoogleNet |
|
||
| -------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||
| Model Version | Inception V1 |
|
||
| Resource | Ascend 910 ;CPU 2.60GHz,56cores;Memory,314G |
|
||
| uploaded Date | 06/09/2020 (month/day/year) |
|
||
| MindSpore Version | 0.3.0-alpha |
|
||
| Dataset | CIFAR-10 |
|
||
| Training Parameters | epoch=125, steps=390, batch_size = 128, lr=0.1 |
|
||
| Optimizer | SGD |
|
||
| Loss Function | Softmax Cross Entropy |
|
||
| outputs | probability |
|
||
| Loss | 0.0016 |
|
||
| Speed | 1pc: 79 ms/step; 8pcs: 82 ms/step |
|
||
| Total time | 1pc: 63.85 mins; 8pcs: 11.28 mins |
|
||
| Parameters (M) | 6.8 |
|
||
| Checkpoint for Fine tuning | 43.07M (.ckpt file) |
|
||
| Model for inference | 21.50M (.onnx file), 21.60M(.geir file) |
|
||
| Scripts | https://gitee.com/mindspore/mindspore/tree/master/model_zoo/googlenet |
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Inference Performance
|
||
|
||
| Parameters | GoogleNet |
|
||
| ------------------- | --------------------------- |
|
||
| Model Version | Inception V1 |
|
||
| Resource | Ascend 910 |
|
||
| Uploaded Date | 06/09/2020 (month/day/year) |
|
||
| MindSpore Version | 0.3.0-alpha |
|
||
| Dataset | CIFAR-10, 10,000 images |
|
||
| batch_size | 128 |
|
||
| outputs | probability |
|
||
| Accuracy | 1pc: 93.4%; 8pcs: 92.17% |
|
||
| Model for inference | 21.50M (.onnx file) |
|
||
|
||
## [How to use](#contents)
|
||
### Inference
|
||
|
||
If you need to use the trained model to perform inference on multiple hardware platforms, such as GPU, Ascend 910 or Ascend 310, you can refer to this [Link](https://www.mindspore.cn/tutorial/zh-CN/master/advanced_use/network_migration.html). Following the steps below, this is a simple example:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# Load unseen dataset for inference
|
||
dataset = dataset.create_dataset(cfg.data_path, 1, False)
|
||
|
||
# Define model
|
||
net = GoogleNet(num_classes=cfg.num_classes)
|
||
opt = Momentum(filter(lambda x: x.requires_grad, net.get_parameters()), 0.01,
|
||
cfg.momentum, weight_decay=cfg.weight_decay)
|
||
loss = nn.SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(sparse=True, reduction='mean',
|
||
is_grad=False)
|
||
model = Model(net, loss_fn=loss, optimizer=opt, metrics={'acc'})
|
||
|
||
# Load pre-trained model
|
||
param_dict = load_checkpoint(cfg.checkpoint_path)
|
||
load_param_into_net(net, param_dict)
|
||
net.set_train(False)
|
||
|
||
# Make predictions on the unseen dataset
|
||
acc = model.eval(dataset)
|
||
print("accuracy: ", acc)
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Continue Training on the Pretrained Model
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# Load dataset
|
||
dataset = create_dataset(cfg.data_path, cfg.epoch_size)
|
||
batch_num = dataset.get_dataset_size()
|
||
|
||
# Define model
|
||
net = GoogleNet(num_classes=cfg.num_classes)
|
||
# Continue training if set pre_trained to be True
|
||
if cfg.pre_trained:
|
||
param_dict = load_checkpoint(cfg.checkpoint_path)
|
||
load_param_into_net(net, param_dict)
|
||
lr = lr_steps(0, lr_max=cfg.lr_init, total_epochs=cfg.epoch_size,
|
||
steps_per_epoch=batch_num)
|
||
opt = Momentum(filter(lambda x: x.requires_grad, net.get_parameters()),
|
||
Tensor(lr), cfg.momentum, weight_decay=cfg.weight_decay)
|
||
loss = nn.SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(sparse=True, reduction='mean', is_grad=False)
|
||
model = Model(net, loss_fn=loss, optimizer=opt, metrics={'acc'},
|
||
amp_level="O2", keep_batchnorm_fp32=False, loss_scale_manager=None)
|
||
|
||
# Set callbacks
|
||
config_ck = CheckpointConfig(save_checkpoint_steps=batch_num * 5,
|
||
keep_checkpoint_max=cfg.keep_checkpoint_max)
|
||
time_cb = TimeMonitor(data_size=batch_num)
|
||
ckpoint_cb = ModelCheckpoint(prefix="train_googlenet_cifar10", directory="./",
|
||
config=config_ck)
|
||
loss_cb = LossMonitor()
|
||
|
||
# Start training
|
||
model.train(cfg.epoch_size, dataset, callbacks=[time_cb, ckpoint_cb, loss_cb])
|
||
print("train success")
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Transfer Learning
|
||
To be added.
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [Description of Random Situation](#contents)
|
||
|
||
In dataset.py, we set the seed inside “create_dataset" function. We also use random seed in train.py.
|
||
|
||
|
||
# [ModelZoo Homepage](#contents)
|
||
Please check the official [homepage](https://gitee.com/mindspore/mindspore/tree/master/model_zoo).
|