4.4 KiB
Example Application: BrowserQwen
We have also developed an example application based on Qwen-Agent: a Chrome browser extension called BrowserQwen, which has key features such as:
- You can discuss with Qwen regarding the current webpage or PDF document.
- It records the web pages and PDF/Word/PowerPoint materials that you have browsed. It helps you understand multiple pages, summarize your browsing content, and automate writing tasks.
- It comes with plugin integration, including Code Interpreter for math problem solving and data visualization.
BrowserQwen Demonstration
You can watch the following showcase videos to learn about the basic operations of BrowserQwen:
- Long-form writing based on visited webpages and PDFs. video
- Drawing a plot using code interpreter based on the given information. video
- Uploading files, multi-turn conversation, and data analysis using code interpreter. video
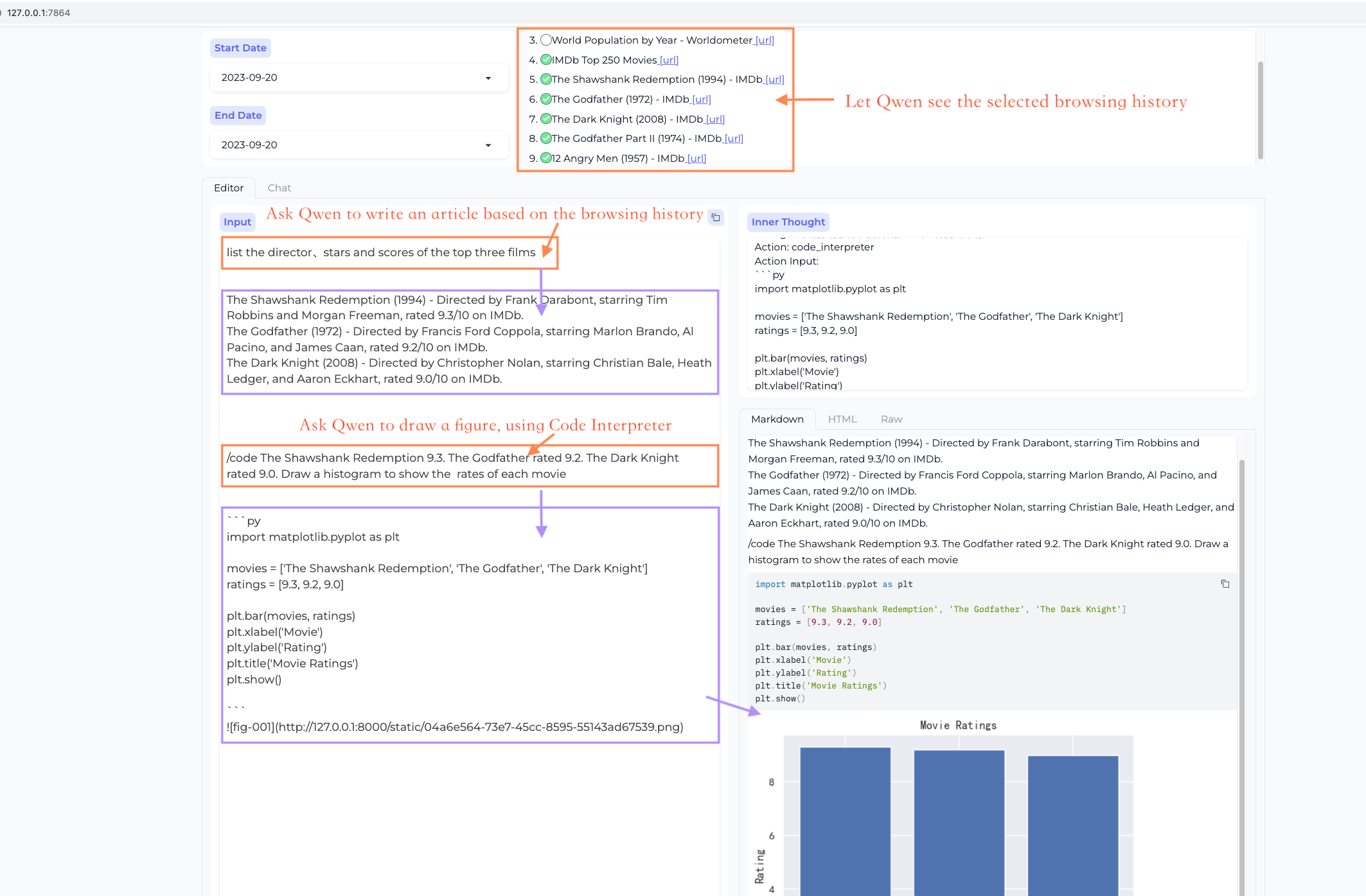
Workstation - Editor Mode
This mode is designed for creating long articles based on browsed web pages and PDFs.

It allows you to call plugins to assist in rich text creation.
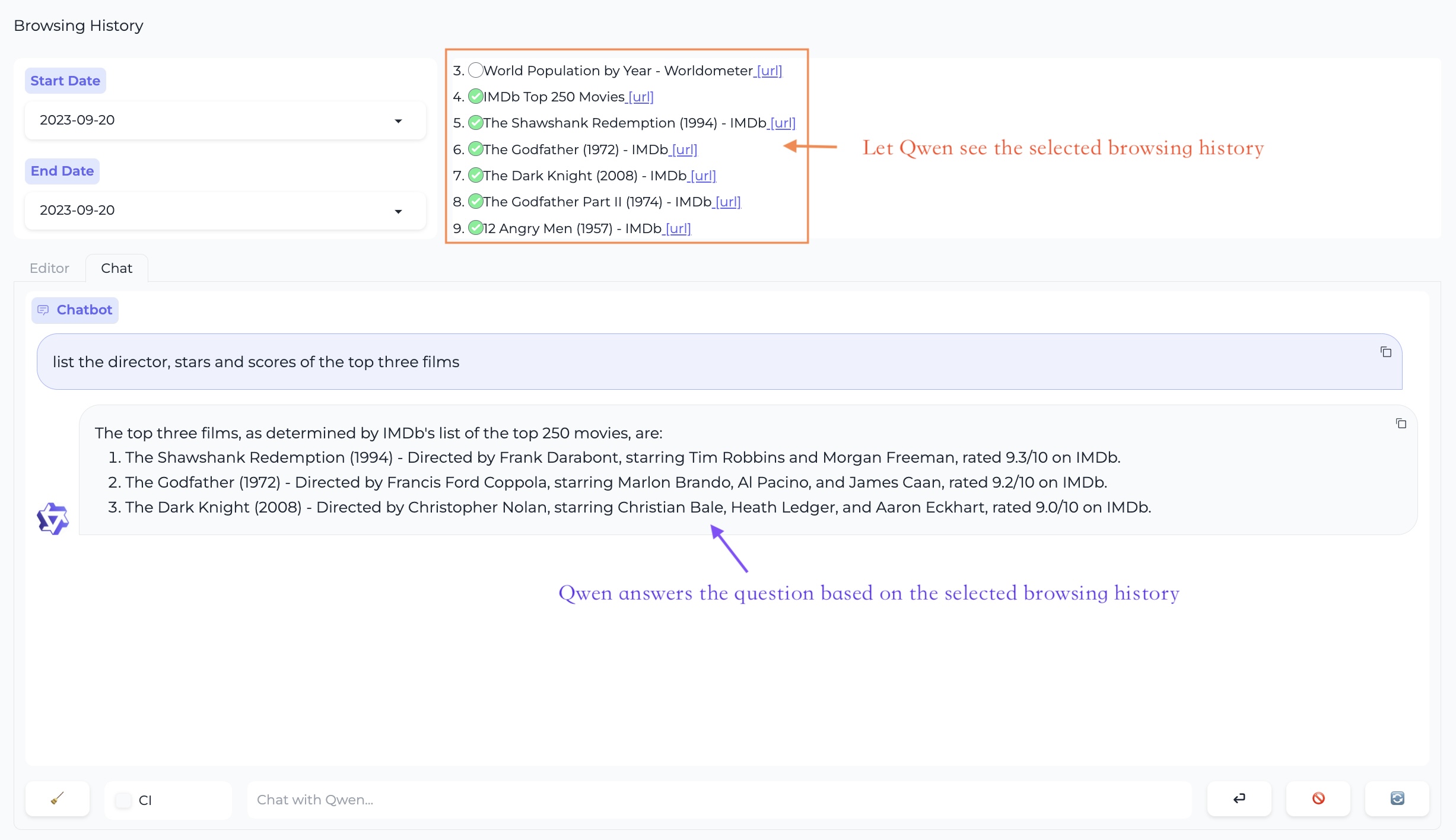
Workstation - Chat Mode
In this mode, you can engage in multi-webpage QA.
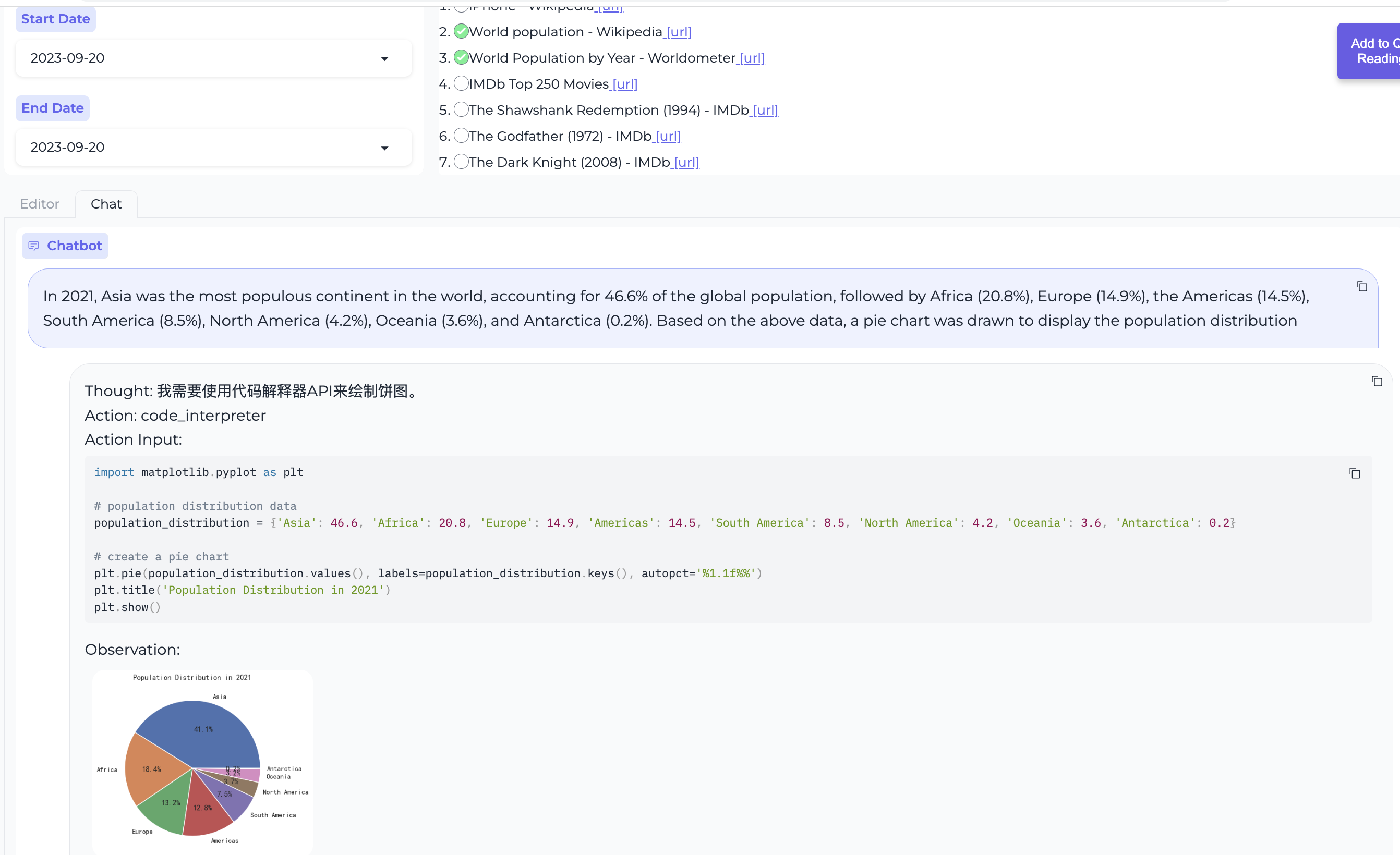
Create data charts using the code interpreter.
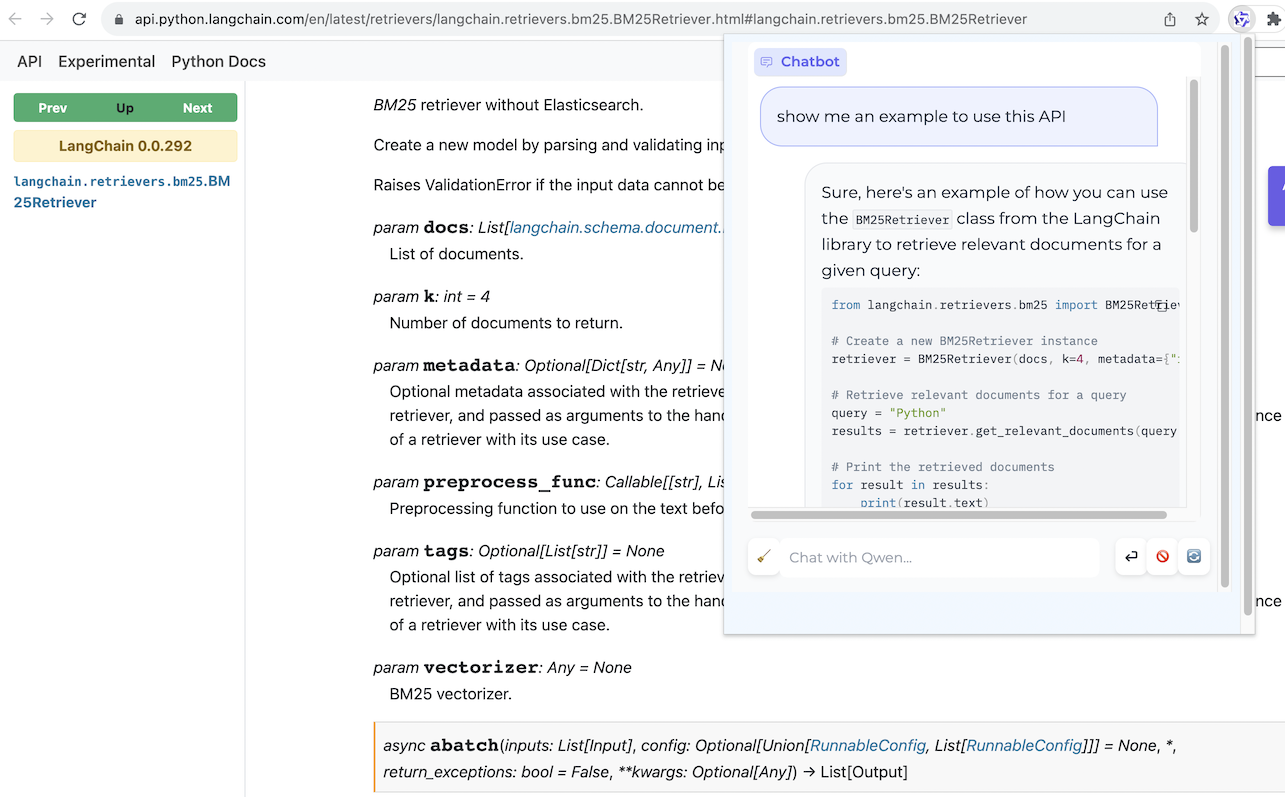
Browser Assistant
Web page QA
PDF document QA

BrowserQwen User Guide
Step 1. Deploy Local Database Service
On your local machine (the machine where you can open the Chrome browser), you will need to deploy a database service to manage your browsing history and conversation history.
If you are using DashScope's model service, then please execute the following command:
# Start the database service, specifying the model on DashScope by using the --llm flag.
# The value of --llm can be one of the following, in increasing order of resource consumption:
# - qwen1.5-7b/14b/72b-chat (the same as the open-sourced Qwen1.5 7B/14B/72B Chat model)
# - qwen-turbo, qwen-plus, qwen-max (qwen-max is recommended)
# "YOUR_DASHSCOPE_API_KEY" is a placeholder. The user should replace it with their actual key.
python run_server.py --llm qwen-max --model_server dashscope --workstation_port 7864 --api_key YOUR_DASHSCOPE_API_KEY
If you are using your own model service instead of DashScope, then please execute the following command:
# Specify the model service, and start the database service.
# Example: Assuming Qwen1.5-72B-Chat is deployed at http://localhost:8000/v1 using vLLM, you can specify the model service as:
# --llm Qwen1.5-72B-Chat --model_server http://localhost:8000/v1 --api_key EMPTY
python run_server.py --llm {MODEL} --model_server {API_BASE} --workstation_port 7864 --api_key {API_KEY}
Now you can access http://127.0.0.1:7864/ to use the Workstation's Editor mode and Chat mode.
Step 2. Install Browser Assistant
Install the BrowserQwen Chrome extension:
- Open the Chrome browser and enter
chrome://extensions/in the address bar, then press Enter. - Make sure that the
Developer modein the top right corner is turned on, then click onLoad unpackedto upload thebrowser_qwendirectory from this project and enable it. - Click the extension icon in the top right corner of the Chrome browser to pin BrowserQwen to the toolbar.
Note that after installing the Chrome extension, you need to refresh the page for the extension to take effect.
When you want Qwen to read the content of the current webpage:
- Click the
Add to Qwen's Reading Listbutton on the screen to authorize Qwen to analyze the page in the background. - Click the Qwen icon in the browser's top right corner to start interacting with Qwen about the current page's content.